A total of 283 cases. The mean age was 38.6 ± 14.1. The male-to-female ratio was 1.05:1 (male, 51.2%).
| 2019 (n=69) | 2020 (n=65) | 2021 (n=42) | 2022 (n=51) | 2023 (n=51) | Total (n=278) |
1ry GN | 25 (36.2%) | 26 (40%) | 21 (50%) | 25 (49%) | 29 (56.9%) | 126 (45.3%) |
2ry GN | 31 (44.9%) | 30 (46.2%) | 17 (40.5%) | 19 (37.3%) | 14 (27.5%) | 111 (39.9%) |
TIN | 6 (8.7%) | 2 (3.1%) | 2 (4.8%) | 2 (3.9%) | 1 (2%) | 13 (4.7%) |
Others | 7 (10.1%) | 7 (10.8%) | 2 (4.8%) | 5 (9.8%) | 7 (13.7%) | 28 (10.1%) |
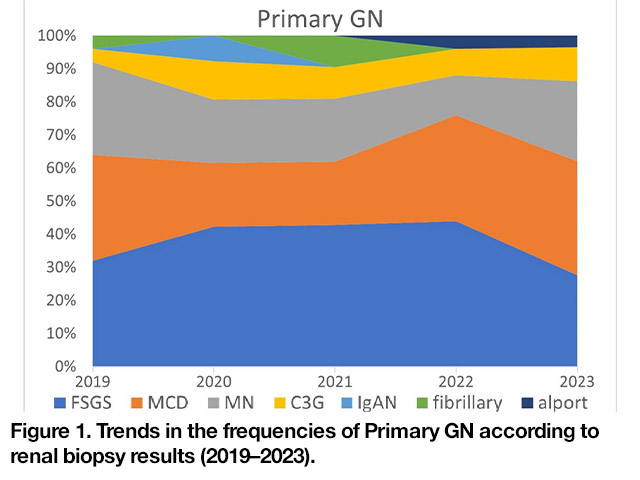
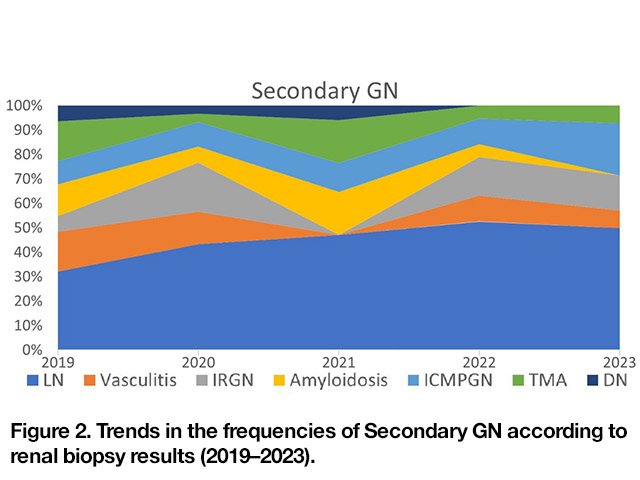
1ry GN, 2ry GN, TIN, and other diagnoses accounted for 45.3%, 39.9%, 4.7%, and 10.1% of cases, respectively. The proportions of 1ry GN in different periods were 36.2.2% (2019), 40% (2020), 50% (2021), 49% (2022) , and 56.9% (2023); 2ry GN accounted for 44.9% (2019), 46.2% (2020) , 40.5% (2021) , 37.3% (2022), and 27.5% (2023); and TIN accounted for 6.7% (2019), 3.1% (2020) , 4.8% (2021) , 3.9% (2022), and 2% (2023)The proportion of PGN in different periods showed a growth trend, while the proportions of SGN declined. FSGS, MCD, and MN were the main causes of 1ry GN, accounting for 37.3%, 27.8%, and 20.6% of total 1ry GN patients, respectively. As shown in [Figure 1] , LN, vasculitis, and IRGN were the main causes of 2ry GN, accounting for 43.2%, 10.8% and 11.7%, respectively. From 2010 to 2018, the proportion of LN increased significantly (32.3% in 2019, 43.3% in 2020, 47.1% in 2021, 52.6% in 2022, and 50% in 2023).
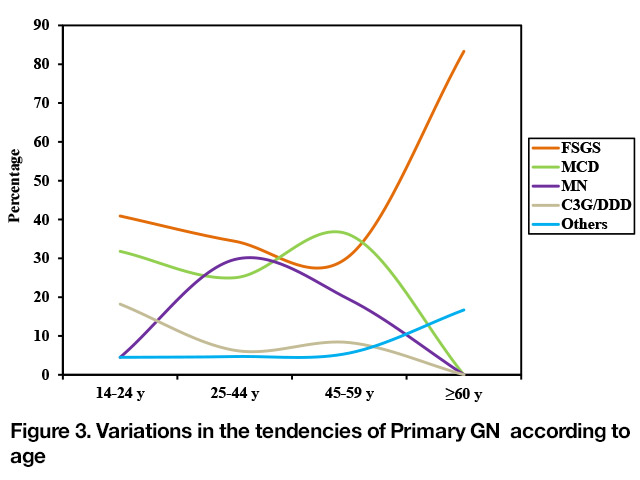
FSGS, MCD, and MN were the main causes of 1ry GN in our study. The proportions of these types varied dramatically with age. FSGS mostly occurs in bimodal fashion as it occurred in 40.9% in 14-24 y age group and 83.3% in elderly patients group ≥ 60 y. meanwhile MN mostly occurred in young patients with a peak in the 25–44years age category (29.7%)
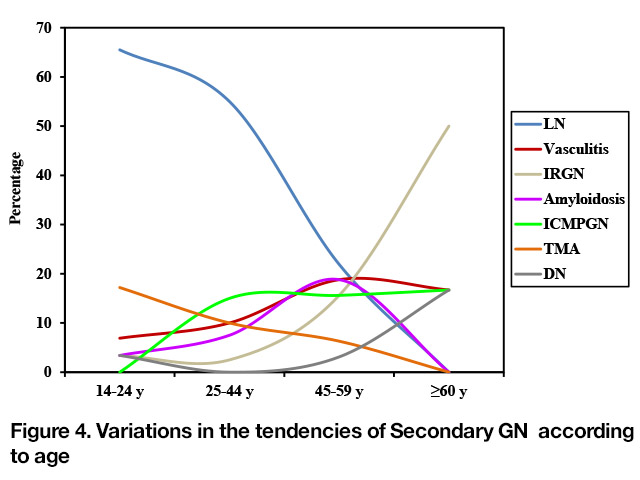
Overall, LN, vasculitis, IRGN were the most common 2ry GN diagnoses. The frequency of LN decrease dramatically with aging reached a peak (65.5%) in the 14–24 years age category and then dropped to 0% in ≥ 60 y. while IRGN frequency increased with age peaking in patients ≥ 60 y (50%).